AI in logistics
AI in logistics: Top 15 present and future applications and use cases.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is significantly transforming the logistics sector by boosting efficiency, lowering costs, and enhancing operational resilience. As I delve into this area, I’ve noticed how AI technologies are providing innovative solutions to persistent challenges, such as unpredictable demand, workforce shortages, and the urgent need for quicker and more dependable deliveries.
A report from McKinsey highlights that AI integration in logistics could create between $1.3 to $2 trillion in economic value annually over the next two decades. This potential for change is both thrilling and challenging as we navigate an increasingly intricate supply chain environment.
Let’s explore some of the current and future AI applications that are reshaping logistics, illustrating how these technologies are being embedded in operations to optimize processes, improve decision-making, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction.
From self-driving vehicles and drones to sophisticated analytics and smart inventory management, AI is set to redefine our approach to logistics and supply chain management.
As I investigate these use cases, it becomes clear that the future of logistics is not solely about embracing new technologies but also about rethinking the entire industry for a more efficient and robust future.
1. Logistics Planning
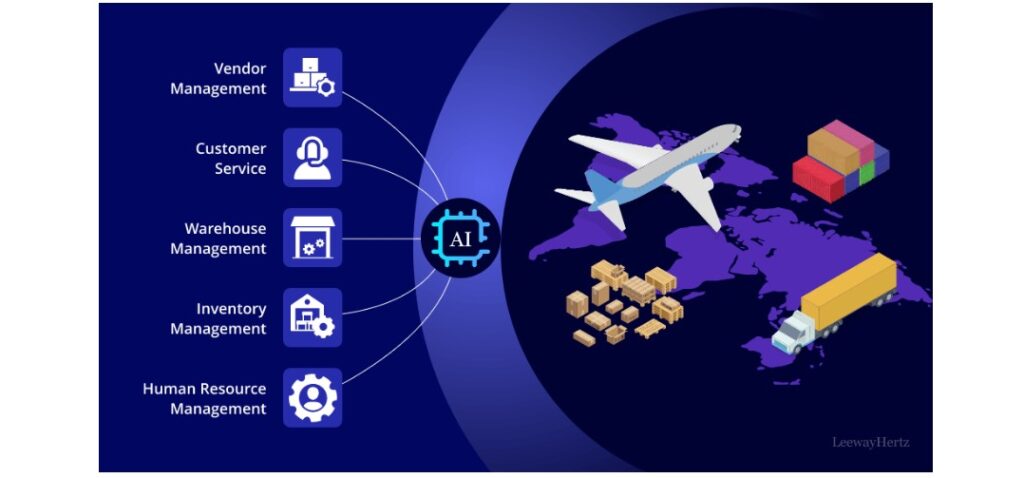
AI In Logistics Planning
Effective logistics planning is crucial to managing supply chain complexity. AI offers advanced predictive capabilities, optimizing planning processes that would be too complex for traditional systems.
Present Applications
Demand Forecasting: AI currently analyzes real-time data, including historical sales patterns, weather conditions, economic indicators, and consumer behavior. This enables businesses to forecast demand with higher accuracy. AI-based demand forecasting models, like deep learning algorithms, reduce forecasting errors by up to 50% compared to older methods like time-series analysis (ARIMA, exponential smoothing). For example, retailers like Walmart and Amazon use AI to better anticipate customer demand during holiday seasons or unexpected global events, adjusting inventory in real-time.
Supply Chain Network Optimization: AI solutions can identify bottlenecks in the supply chain and provide recommendations for optimizing routes, schedules, and supply flows. Current platforms use AI to assess supplier reliability, adjust inventory levels, and manage global sourcing more effectively.
Future Applications
Adaptive Demand Forecasting: Future AI systems will continuously update forecasts in real-time, reacting to changes in market demand almost instantaneously. For example, during sudden disruptions like a global pandemic or natural disaster, AI will recalibrate inventory and logistics in response to new patterns.
End-to-End Supply Chain Automation: AI will integrate across the entire supply chain, autonomously coordinating everything from procurement and production schedules to warehouse management and distribution. This integration will ensure that any disruptions in one part of the chain trigger automatic adjustments in others, minimizing delays and wastage.
Predictive Inventory Management: AI will go beyond simple forecasting to optimize inventory flow dynamically. Algorithms will predict which warehouses or distribution centers will experience demand spikes and shift resources accordingly. Companies like Zara already employ AI to manage inventory across stores, ensuring they never over- or under-stock.
2. Automated Warehousing
AI is making warehouses smarter by automating various aspects of operations, from sorting and picking to maintenance. Warehousing will become almost entirely automated in the near future, driven by AI’s capacity to manage complex tasks.
Present Applications
AI-Powered Robots: In the present, AI-powered robots and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are performing routine tasks like transporting goods, picking items, and restocking shelves. Amazon’s Kiva robots are a prime example, improving efficiency and reducing order processing time. These robots can autonomously navigate warehouses, ensuring optimal paths and minimal energy use.
Automated Sorting Systems: AI-powered computer vision and machine learning algorithms are being used to sort packages based on size, shape, or destination, enabling rapid sorting even during peak demand periods.
Visual Inspection and Quality Control: AI systems are currently used to inspect products for defects or damage. For instance, automated inspection systems equipped with AI can detect damage in goods with high precision before they are dispatched.
Future Applications
Fully Autonomous Warehouses: In the future, AI-driven robots will not only perform repetitive tasks but also work alongside human workers in a collaborative manner. They will execute more complex tasks, like machine repairs, warehouse inventory management, and even learning new processes from humans through reinforcement learning techniques. These fully autonomous warehouses will run 24/7, significantly reducing human intervention.
Predictive Maintenance of Warehouse Equipment: While current AI systems predict mechanical failures based on historical data, future AI will be capable of real-time monitoring and self-healing systems. These machines will have embedded sensors that predict wear and tear, replacing parts automatically before breakdowns occur. This will minimize downtime, resulting in continuous warehouse operation.
Dynamic Inventory Allocation: In future smart warehouses, AI will allocate inventory based on real-time demand patterns. Instead of static inventory storage, AI will predict which items need to be close to dispatch points or reorganize storage locations to reduce picking time. This dynamic system will evolve with fluctuating customer preferences.
3. Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Autonomous systems represent one of the most promising frontiers for AI in logistics. Self-driving trucks and drones are expected to disrupt last-mile delivery and reduce human reliance.
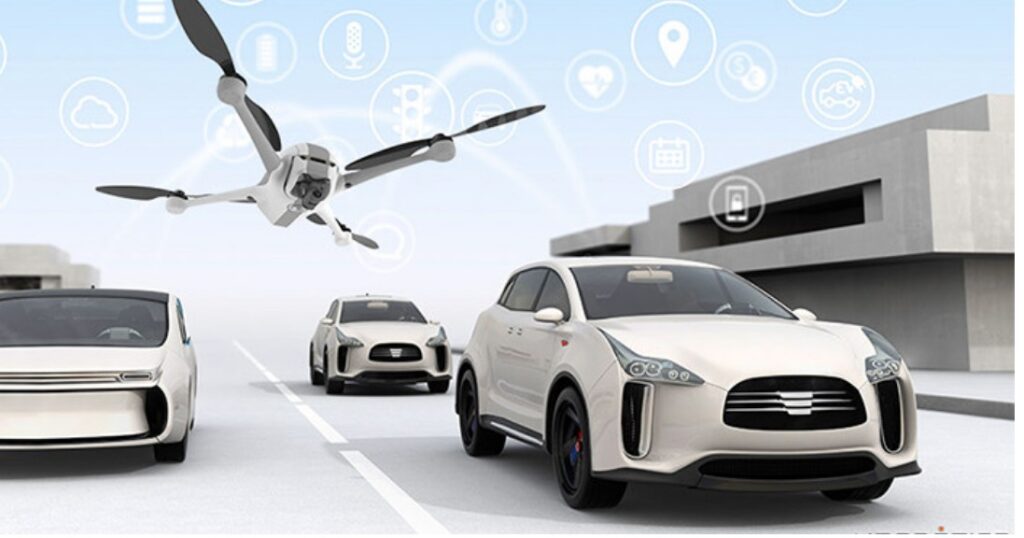

Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Present Applications
Self-Driving Trucks: Companies like Waymo, Tesla, and TuSimple are already deploying autonomous trucks for limited commercial use. These trucks use AI-powered sensors, cameras, and radar to navigate highways, performing long-haul deliveries with little or no human intervention. Today, many of these trucks still require a human driver as a backup, but the trend toward full autonomy is advancing.
Delivery Drones: Companies such as UPS and Zipline have begun using drones for small-scale delivery operations, particularly in remote or hard-to-reach areas. Drones use AI to navigate complex environments, optimizing routes and avoiding obstacles autonomously.
Future Applications
Fully Autonomous Freight Transport: By 2030, we expect to see self-driving trucks handling the majority of long-distance freight transport. AI systems will autonomously optimize fuel consumption, choose the most efficient routes, and handle loading and unloading. AI will also manage fleet coordination, ensuring that deliveries across entire countries or regions are conducted with minimal human involvement.
Autonomous Last-Mile Delivery: Delivery drones and robots will become standard for last-mile deliveries, especially in urban areas. These AI-driven machines will handle package deliveries to homes and businesses autonomously, reducing delivery times from hours to minutes. These systems will be equipped with real-time machine learning models that adapt to changing environmental conditions like traffic, weather, and customer availability.
Platooning Technology: In the future, AI will allow trucks to form platoons — groups of self-driving trucks traveling closely together. AI will optimize the distance between vehicles to reduce wind resistance and fuel consumption. These platoons will communicate wirelessly, reacting to each other’s movements in real-time to maintain optimal driving conditions.
4. AI-Driven Analytics for Logistics
Analytics powered by AI enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimizing everything from pricing to route planning and customer service. AI-driven analytics are transforming logistics into a more efficient and responsive industry.
Present Applications
Dynamic Pricing: AI-powered algorithms are currently adjusting logistics pricing in real-time based on various factors such as demand, traffic, delivery schedules, and resource availability. For example, FedEx and UPS use dynamic pricing models to account for seasonal fluctuations in shipping costs.
Real-Time Route Optimization: AI analyzes real-time data on traffic, weather, and road conditions to suggest the most efficient routes for delivery trucks, reducing fuel costs and delivery times. AI-based route optimization tools, such as those used by UPS’s ORION system, have already saved millions of miles in delivery travel.
Future Applications
Hyper-Personalized Pricing Models: In the future, AI will enable highly personalized pricing strategies tailored to individual customers’ purchasing behaviors and preferences. AI will analyze vast datasets on customer profiles and past transactions to offer personalized discounts or dynamic pricing that maximizes profit while ensuring customer satisfaction.
Real-Time, Autonomous Freight Management: AI-driven systems will autonomously allocate freight across shipping carriers based on real-time cost and performance analysis. AI will continuously monitor the entire logistics network, choosing optimal combinations of routes, transportation modes (truck, rail, air, or sea), and schedules to achieve cost and time savings.
AI in Predictive Supply Chain Analytics: AI will predict potential supply chain disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, political unrest) with increasing accuracy, allowing companies to take proactive steps like rerouting shipments, adjusting orders, or finding alternative suppliers before problems arise.
5. Customer Service and Back-Office Automation
AI is transforming customer service and back-office operations in logistics, reducing manual tasks, enhancing decision-making, and improving customer experience.
Present Applications
AI-Powered Chatbots: Today, AI-powered chatbots handle routine customer inquiries such as shipment tracking, order changes, and basic troubleshooting. These systems, like the one used by FedEx, reduce the need for human customer service agents while offering fast, accurate responses.
Automating Document Processing: AI is already automating routine back-office tasks such as invoice processing, bills of lading generation, and contract verification. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms are used to scan and extract key data from documents, saving businesses time and reducing human error.
Future Applications
AI-Driven Hyperautomation: In the future, AI will not only handle simple administrative tasks but will also automate entire workflows, from order processing and inventory management to compliance and auditing. Hyperautomation combines AI with robotic process automation (RPA) to create fully autonomous back-office operations.
Advanced Customer Interaction Systems: AI-driven virtual assistants will become increasingly conversational and sophisticated, handling complex customer queries, complaints, and even order changes. Future AI systems will be able to understand customer emotions, adjust their tone accordingly, and offer tailored solutions.
6. Sustainable and Green Logistics
AI is playing an increasingly important role in promoting sustainability by optimizing energy use, reducing emissions, and enhancing resource efficiency across logistics networks.
Present Applications
Optimized Route Planning for Emission Reduction: AI-driven systems are already helping logistics companies minimize fuel consumption by optimizing delivery routes to reduce idle time, traffic, and unnecessary stops. By utilizing predictive traffic models, logistics giants like DHL and UPS are cutting down on emissions and fuel costs.
AI for Waste Reduction: AI is helping logistics companies minimize waste through smart packaging solutions that optimize packaging sizes and reduce material usage. For instance, companies are leveraging AI to recommend smaller, more efficient packaging configurations based on the size and shape of items being shipped, reducing excess material waste and lowering carbon footprints.
Future Applications
Carbon-Neutral Delivery Systems: AI will help logistics providers become fully carbon-neutral by automating decisions that reduce carbon footprints, such as dynamically adjusting shipping routes based on real-time traffic and environmental data. AI will also manage hybrid and electric vehicle fleets to maximize efficiency and energy conservation. Future systems could suggest the best times to charge electric trucks and drones using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
Circular Supply Chain Optimization: AI will help build circular supply chains, where products and materials are reused, refurbished, or recycled instead of disposed of. In this system, AI will track materials and products throughout their life cycles, enabling businesses to reclaim valuable resources at the end of product life, thus minimizing waste and promoting sustainability.
7. Hyper-Personalized Last-Mile Delivery Solutions
AI is revolutionizing the “last-mile” segment of logistics by providing personalized, efficient, and flexible delivery options for consumers.
Present Applications
Dynamic Delivery Windows: AI systems today offer customers the option to select delivery windows that best suit their schedules. These dynamic delivery windows, like those offered by Amazon, improve customer satisfaction by reducing the chances of missed deliveries. AI adjusts delivery routes in real-time based on customer preferences.
Automated Locker Systems: Companies like Amazon and UPS use AI to route packages to smart lockers, providing customers with flexibility in picking up deliveries. AI ensures the lockers are optimally located based on customer density and accessibility, reducing the need for doorstep deliveries.
Future Applications
AI-Driven Personal Delivery Assistants: Future AI systems will learn customer preferences over time, offering hyper-personalized delivery options such as preferred delivery times, days, and locations. These AI-driven systems will autonomously reroute packages in real-time based on a customer’s changing schedule or preferences, ensuring seamless last-mile deliveries.
Autonomous Delivery Robots and Drones: AI-powered autonomous delivery robots and drones will soon become standard for last-mile deliveries, especially in densely populated urban areas. These systems will offer ultra-fast, same-day delivery by efficiently navigating crowded cities or remote locations, all while optimizing energy consumption.
8. Predictive Fleet Maintenance
AI is transforming fleet management by predicting maintenance needs, thereby reducing downtime, preventing failures, and optimizing vehicle usage across logistics fleets.
Present Applications
Telematics and Predictive Maintenance: Currently, AI is used to monitor vehicle performance in real-time through telematics, which collects data on vehicle speed, fuel usage, engine health, and driving behavior. AI analyzes this data to predict when maintenance is required, preventing breakdowns and reducing repair costs. Companies like FedEx are using these predictive maintenance models to extend the lifespan of their fleet vehicles.
Dynamic Maintenance Scheduling: AI-powered platforms predict optimal maintenance times by analyzing fleet usage patterns, traffic conditions, and weather data to reduce fleet downtime.
Future Applications
Self-Healing Vehicles: Future fleets will feature AI-embedded vehicles that detect issues autonomously and initiate real-time self-diagnosis. AI will order spare parts, schedule repairs, or even activate self-repair functions (for minor problems) without human intervention, reducing fleet downtime significantly.
AI-Powered Fleet Management Systems: AI will create autonomous fleet management systems that automatically allocate vehicles to different tasks based on real-time usage data, vehicle health, and maintenance needs. These systems will enhance fleet longevity, reduce operational costs, and ensure optimal fleet performance across the entire supply chain.
9. Intelligent Risk Management
AI is helping logistics companies manage risk more effectively by predicting disruptions, improving decision-making, and automating compliance.
Present Applications
Predicting Supply Chain Disruptions: AI is currently being used to forecast potential supply chain disruptions by analyzing data from various sources, such as geopolitical developments, weather forecasts, and transportation strikes. AI systems help businesses mitigate these risks by suggesting alternative routes or suppliers in advance.
AI for Compliance and Regulation: Logistics companies use AI-powered systems to ensure compliance with customs regulations, trade laws, and shipping standards. Automated systems can flag discrepancies in documentation, reducing the risk of non-compliance fines.
Future Applications
Real-Time Global Supply Chain Risk Monitoring: AI systems will continuously scan and analyze global risk factors, including economic conditions, political unrest, and environmental factors, providing real-time alerts and actionable insights. Businesses will be able to proactively adjust their supply chains to mitigate disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions, pandemics, or other unforeseen events.
Blockchain Integration for Risk Management: In the future, AI will integrate with blockchain technology to create transparent and immutable supply chain records. This combination will provide enhanced security, ensuring that all transactions and movements within the supply chain are accurately tracked and verified, reducing fraud and mismanagement.
10. AI-Powered Logistics Talent Management
The logistics workforce is evolving, and AI is being used to optimize talent management through automation, workforce planning, and productivity monitoring.
Present Applications
Workforce Planning: AI is helping logistics companies match labor supply with demand, especially during peak seasons. By analyzing historical staffing data, sales forecasts, and delivery schedules, AI can recommend the optimal number of workers needed at any given time. Retailers and 3PL providers already use AI systems to manage labor in warehousing and transportation operations.
Employee Productivity Monitoring: AI-powered tools are currently tracking employee productivity, particularly in warehouses, where performance metrics like speed, accuracy, and efficiency are automatically logged.
Future Applications
AI-Driven Autonomous HR Systems: In the future, AI will manage the entire talent lifecycle in logistics, from recruitment to workforce optimization. AI will predict staffing needs, recommend training programs, and provide personalized employee development plans. Autonomous HR systems will assess individual performance and suggest team structures that optimize productivity.
Exoskeleton and Wearable AI for Enhanced Worker Performance: AI-powered exoskeletons and wearable devices will assist warehouse workers in physically demanding tasks, reducing injuries and increasing efficiency. Wearable AI devices will monitor worker health and safety in real-time, alerting supervisors to potential hazards or recommending changes in work conditions to avoid accidents.
11. Real-Time Inventory Optimization
AI is advancing the field of inventory management, enabling companies to maintain optimal stock levels, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by leveraging real-time data and predictive analytics.
Present Applications
Automated Inventory Management Systems: AI-powered systems are currently helping companies automate their inventory management by tracking stock levels in real-time and using predictive analytics to forecast future demand. For example, Amazon and Walmart leverage AI to predict the exact quantity of products needed in their warehouses, avoiding overstocking and stockouts.
AI-Powered Demand Forecasting: Retailers and manufacturers are using AI algorithms to analyze historical sales data, market trends, and seasonality to predict future demand for products, ensuring that the right amount of inventory is stocked at the right locations.
Future Applications
Fully Autonomous Inventory Replenishment: In the future, AI systems will automatically manage inventory replenishment by dynamically adjusting stock levels based on real-time demand, supplier lead times, and even weather forecasts. AI will autonomously place orders with suppliers and adjust shipment schedules, ensuring optimal stock levels at all times.
AI-Driven Warehouse Robotics for Inventory Management: Warehouse robots, powered by AI, will autonomously track inventory, update stock levels, and move items between locations in real-time. These robots will work in tandem with AI inventory systems to ensure that shelves are stocked efficiently, enabling faster fulfillment and reducing human error in inventory processes.
12. Personalized Customer Experiences in E-Commerce Logistics
AI is enabling logistics providers to offer more personalized, customer-centric services, transforming how goods are ordered, shipped, and delivered in e-commerce.
Present Applications
Personalized Delivery Options: E-commerce platforms like Shopify and Amazon are using AI to provide personalized delivery options based on individual customer preferences. AI tailors shipping methods and delivery times to match each customer’s preferences, improving the customer experience.
AI-Powered Chatbots for Customer Support: AI chatbots are currently helping customers track shipments, resolve delivery issues, and answer frequently asked questions, improving service efficiency. AI can provide real-time updates on the status of an order and predict delivery times more accurately.
Future Applications
Proactive AI-Driven Customer Notifications: AI will proactively notify customers about delays, changes in delivery times, or alternative delivery options based on their location, preferences, and schedule. These systems will predict potential disruptions and offer solutions, such as changing the delivery location or time to fit the customer’s needs.
Virtual Shopping Assistants with Real-Time Delivery Insights: Future AI systems will integrate deeply into e-commerce platforms, offering personalized product recommendations based on past purchases and real-time delivery insights. AI will inform customers of estimated delivery times for products before they purchase, optimizing the entire shopping and logistics experience.
13. Cold Chain Logistics Optimization
AI is enhancing the management of temperature-sensitive goods (e.g., pharmaceuticals, perishable foods) by ensuring that products are stored and transported under optimal conditions throughout the entire logistics chain.
Present Applications
Temperature Monitoring with IoT Sensors: AI systems currently monitor temperature-sensitive shipments using IoT devices that track environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and light exposure. AI analyzes this data to detect any anomalies and ensures that goods are transported in optimal conditions.
AI-Driven Route Optimization for Perishables: Companies involved in cold chain logistics are using AI to optimize delivery routes, minimizing the time that perishable goods spend in transit. AI models consider traffic, weather, and road conditions to suggest the fastest routes for cold chain deliveries.
Future Applications
Predictive Cold Chain Monitoring: AI will enhance cold chain logistics by predicting potential disruptions such as temperature deviations or equipment malfunctions. AI systems will autonomously reroute shipments or adjust refrigeration settings to ensure the safe transportation of sensitive products, minimizing the risk of spoilage.
Blockchain and AI Integration for Traceability: In the future, AI will integrate with blockchain technology to create a fully transparent cold chain, where every stage of the transportation process is logged and verified. This will ensure that temperature-sensitive products like vaccines or fresh produce are handled correctly, with AI continuously monitoring and verifying conditions throughout the supply chain.
14. Dynamic Warehousing Solutions (On-Demand Warehousing)
AI is revolutionizing warehousing by enabling dynamic, on-demand storage solutions, allowing businesses to flexibly scale their storage needs based on demand.
Present Applications
AI-Driven Warehouse Space Allocation: AI is currently being used to optimize warehouse space utilization by predicting incoming inventory levels and allocating space dynamically. Platforms like Flexe use AI to match businesses with available warehouse space, allowing them to scale up or down as needed.
Robot-Assisted Picking and Sorting: Warehouses are using AI-powered robots to pick and sort products based on real-time orders, reducing human labor and improving efficiency. These robots work alongside AI algorithms that determine the most efficient way to fulfill customer orders based on product location and shipping destination.
Future Applications
On-Demand Warehousing Networks: AI will create fully autonomous on-demand warehousing networks where businesses can instantly book and access warehouse space as needed. These systems will dynamically adjust warehouse space availability based on market trends, shipping volume, and customer demand, allowing companies to expand or contract storage capacity in real-time.
AI-Driven Warehouse Location Optimization: Future AI models will analyze demand patterns and transportation costs to recommend the most strategic locations for temporary or permanent warehousing. This will enable logistics providers to quickly establish fulfillment centers in high-demand regions, reducing delivery times and costs.
15. Real-Time AI-Enhanced Visibility for Global Supply Chains
AI is transforming how logistics companies gain visibility into their supply chains, providing real-time insights and predictive capabilities across global networks.
Present Applications
Real-Time Shipment Tracking: AI is currently used to provide real-time visibility into the location and status of shipments. AI systems track goods across every stage of the supply chain, allowing logistics managers to monitor their movement and predict arrival times accurately.
Supply Chain Risk Assessment: AI systems today are analyzing geopolitical, economic, and environmental data to assess potential risks to the supply chain. AI flags potential disruptions like natural disasters or political unrest, allowing logistics managers to take proactive measures.
Future Applications
AI-Driven Global Supply Chain Control Towers: In the future, AI-powered control towers will provide end-to-end visibility into global supply chains. These systems will analyze real-time data from multiple sources, including shipping routes, weather patterns, customs data, and supplier conditions, to provide a comprehensive view of the supply chain’s health and performance.
Self-Correcting Supply Chains: AI will enable self-correcting supply chains, where disruptions are automatically detected and addressed without human intervention. AI will autonomously reroute shipments, reallocate resources, and notify suppliers in real-time, ensuring continuous flow and minimizing downtime across global networks.
In conclusion: the future of AI in logistics holds immense promise, with the potential to revolutionise the industry by driving efficiency, cutting costs, and improving overall operational resilience. As AI continues to advance, we will see even greater integration of technologies such as autonomous vehicles, predictive analytics, and intelligent inventory management systems, all working together to streamline the supply chain and meet growing demands for faster, more reliable deliveries.
What excites me most about this transformation is how AI empowers logistics companies to make smarter, data-driven decisions, optimise resource allocation, and overcome long-standing challenges like fluctuating demand and labour shortages. As we look to the future, it’s clear that AI will be a critical driver of innovation in logistics, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and enabling businesses to operate more effectively in a rapidly evolving market.
By embracing these AI-driven advancements, companies can position themselves for long-term success, staying ahead of the competition while delivering exceptional service to customers. The logistics industry is on the brink of a major shift, and AI is the key to unlocking its full potential.